3 geospatial AI trends to keep your eye on
Here we are in the year of AI! So it's fitting that we kick off this blog with a peek at the top trends in geospatial AI. This is a field that is a rapidly evolving and changing, with new trends emerging all the time. Here are just some to look out for.
By Laura Jones | 24th May 2023
3D mapping and modeling
3D mapping and modelling has become increasingly popular in geospatial AI, allowing for the creation of highly detailed and accurate digital representations of real-world environments. This technology has numerous applications, from urban planning to disaster response.
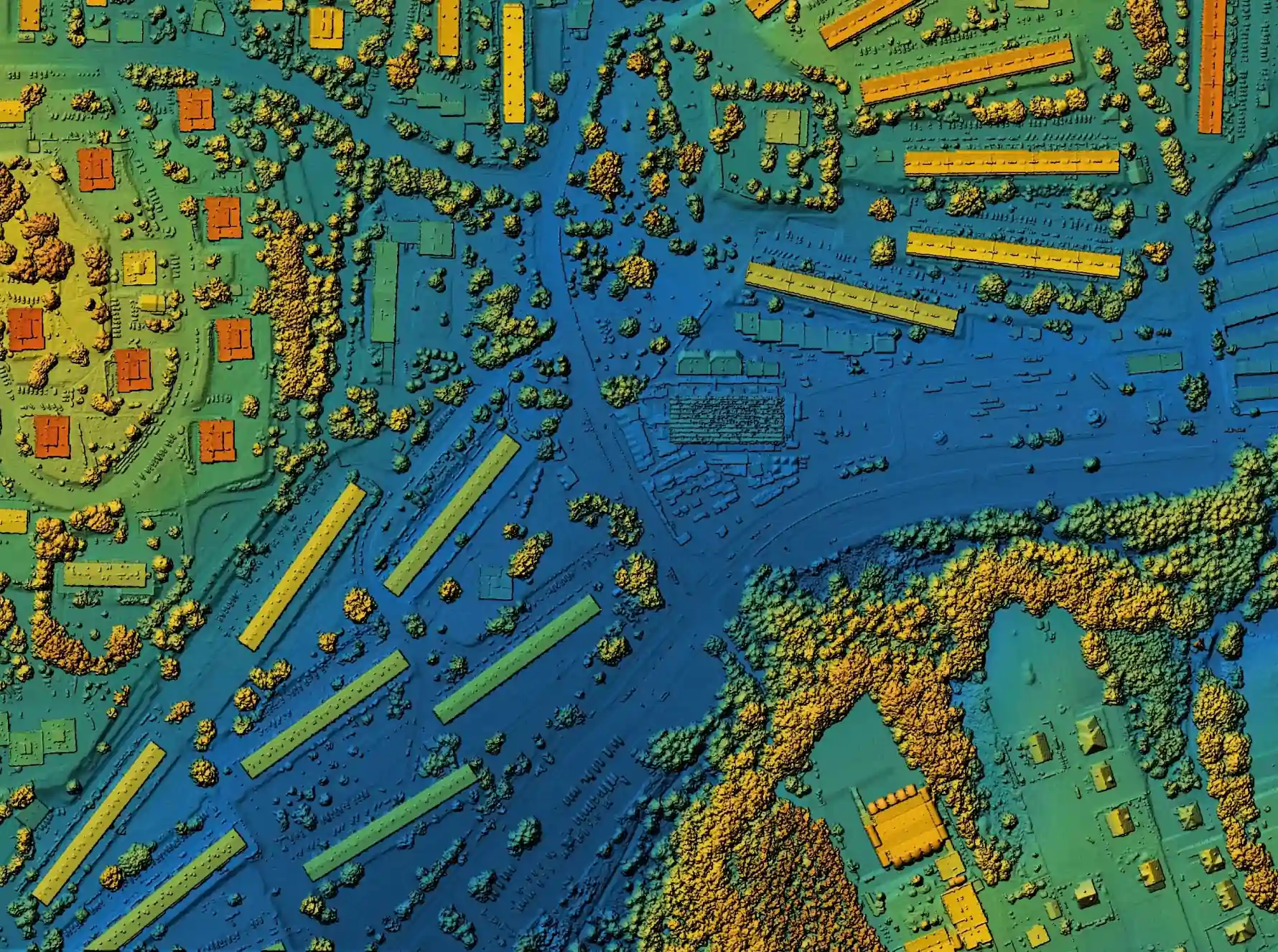
This year a new AI framework called InfiniCity has been developed by a multi-university collaboration that can generate 3D virtual cities with no boundaries. This framework uses three steps to create these environments, starting with generating 2D maps of different sizes, converting them to 3D structures, and texturizing and rendering them as 2D images. This means that users can interact with and edit these virtual environments. InfiniCity has been tested and shows promising results, which could have significant applications in creating virtual environments for training autonomous systems or creating realistic, immersive experiences.
Also being rolled out this year is Google's new Immersive View feature for Maps, which uses AI and AR to create a digital representation of the real world by combining street view and aerial images. This feature is now available in London, Los Angeles, San Francisco, New York, and Tokyo, allowing users to navigate routes and find nearby landmarks, such as ATMs, restaurants, parks, and transit stations. With Immersive View and Live View, users can easily find points of interest while on the street, and these features are designed to make exploring cities easier and more efficient for users.
LiDAR Technology
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is an amazing technology that uses laser beams to measure distances and create detailed 3D maps of the environment. It works by sending out a laser beam and measuring the time it takes for the beam to bounce back after hitting an object. By doing this repeatedly, the technology can create a detailed 3D map of the environment, including the shapes and distances of objects in the scene.

Dutch company Aerial Precision incorporates artificial intelligence software into its proprietary drone-mounted LiDAR system, to register 2 million datapoints per second. This software processes the data in real time meaning post-processing, a long-time industry norm will no longer be required in all instances.
LiDAR is used in a variety of applications, such as mapping the Earth's surface, creating topographic maps, and surveying construction sites. Its also used in autonomous vehicles, where it helps the vehicle "see" its environment by creating a real-time 3D map of the surroundings.
As reported by miragenews.com LiDAR is being implemented as a safety mechanism for snow-plough operations in Hokkaido, Japan. Snow is usually ploughed at night and human guides ensure the path is clear of pedestrians. A collaboration between Hokkaido University and NICHIJO Corporation is developing an AI enabled “human detection” sensor by leveraging the combined power of LiDAR, RGB and thermal sensors. This builds a complete 3D picture of the surroundings, any heat-emitting obstacles in the vicinity as well as the ploughs own position to ensure the path is clear. The project is aimed at eventually developing autonomous snow ploughs.
Real-time Data Analysis
Within the context of geospatial AI, real-time data analysis is particularly important because it allows for the quick and accurate analysis of spatial data. With the use of sensors and other data collection tools, geospatial AI can collect large amounts of data in real-time, such as weather conditions, traffic patterns, and other environmental factors. This data can then be analysed in real-time, allowing for rapid decision-making and response to changing conditions.

For example, real-time data analysis can be used to monitor traffic patterns and congestion in real-time, helping to improve traffic flow and reduce congestion. It can also be used to monitor weather conditions and predict severe weather events, allowing for early warning systems and better disaster response planning.
To Illustrate, geospatial analytics company, Heavy.ai leverages its capabilities to digest and analyse satellite imagery and other geospatial data to create detailed maps and 3D models of affected areas, which can help emergency responders navigate the terrain and plan their response. The platform's analytics capabilities can also be used to track the movement of people and resources in real-time, allowing for more efficient coordination and allocation of resources.